A search engine is a tool which aids the user in locating information on the internet by keying in keywords. It searches its database and shows the most relevant results within seconds. Popular examples include Google and Bing.
What Is a Search Engine?
A search engine is a set of programs that helps users find information on the internet by matching keywords with data stored in its database. It is mainly used to access and retrieve content from the World Wide Web quickly and efficiently.
How Do Search Engines Work?
Search engines like Google work in three main steps. First, crawling takes place, where bots discover new and updated webpages by following links. Next is indexing, in which the search engine analyses and stores page content in a database so it can be understood and retrieved later. Finally, during searching and ranking, the engine matches user queries with indexed pages and ranks results based on relevance, keywords, backlinks, and authority.
Some search engines focus on specific content types, regions, or individual websites, making search results more targeted and useful.
How Search Engines Rank Results
Search engines rank results by analysing several key factors. They first understand search intent by interpreting the meaning of a user’s query. Next, they check relevance by matching keywords in the query with webpage content. Quality and trustworthiness are measured through signals like authoritative backlinks. Usability factors such as mobile-friendliness and page speed also affect rankings. Search engines may use user data and engagement metrics to personalise and refine results.
Content creators use SEO to optimise these factors and improve a page’s visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs).
Goal of Online Search Platform
The main goal of an online search platform is to help users quickly find accurate and relevant information online. Ranking results depend on quality, relevancy, and authority to make the online search platform provide users with the necessary information.
Beyond helping users, online search platforms also have secondary goals, such as allowing website owners to monetise traffic through ads and collect data like click patterns and search behaviour. However, achieving these goals depends on maintaining user trust.
Search engines build trust in several ways:
- Organic Results: Unpaid search results are generally seen as more reliable than ads.
- Authority: High-quality content and backlinks from reputable sources increase credibility.
- Privacy: Engines like DuckDuckGo protect user data and avoid personalised biases, providing unbiased search results.
By balancing relevance, quality, and user trust, search engines aim to deliver the best possible experience for every search.
How Do Search Engines Make Money
Search engines generate revenue through several key methods while providing free access to users:
- Pay-Per-Click Ads (PPC): Advertisers pay every time a user clicks on an ad displayed on search results or partner websites. Popular keywords and highly targeted searches often cost more.
- User Data: Search engines collect information such as search history, location, and device data. This helps them create user profiles to serve personalised and targeted ads, which advertisers pay a premium for.
- Contextual Advertising: Ads are shown based on the user’s current search or the content of a webpage. For example, a search for “laptops” may trigger ads for computer accessories or related products.
- Affiliate Links and Partnerships: Some search engines earn commissions when users click on affiliate links or make purchases through partner websites.
- Donations: Certain nonprofit or privacy-focused search engines rely on voluntary user donations to fund their operations.
By combining advertising, data monetisation, affiliate programs, and donations, search engines turn everyday searches into profitable revenue streams while continuing to provide valuable search services.
How Do Search Engines Personalise Results?
Search engines personalise results to provide users with content that is more relevant to their preferences, habits, and location. Personalisation is achieved by creating digital profiles based on data collected from the devices and applications that users use to access the search engine. This allows search engines to tailor search results, ads, and recommendations to each individual.
Types of Data Collected
Search engines gather a wide range of user data, including:
- Search History: Past searches and clicked results help predict what a user might be interested in.
- Search Date and Time: Patterns in when users search can influence the relevance of results.
- Location Information: Geo-location data helps provide localised results, such as nearby businesses or region-specific news.
- Audio Data: Voice searches from devices like smartphones and smart speakers are analysed.
- User ID and Device Identification: Accounts and devices are tracked to maintain personalised settings across sessions.
- IP Address: Helps determine approximate location and detect suspicious activity.
- Device Diagnostic Data: Information about the device used, such as operating system and browser type.
- Contact Lists and Purchase History: Certain search engines may incorporate this data to suggest relevant products or services.
Role of Cookies
Cookies are small text files sent from websites to a user’s browser to track browsing activity and preferences. An online search platform uses cookies to:
- Remember login information and passwords
- Save language and regional preferences
- Maintain content filters and session settings
- Track browsing history to personalise search results and ads
Cookies allow search engines to improve the user experience by making searches faster, more relevant, and more personalised.
Private Browsing and Its Limitations
Using private or incognito browsing can prevent tracking at the device level. In this mode:
- Search history and session information are not saved
- Cookies are deleted after the session ends
However, private browsing does not hide activity from:
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
- Employers (if using a work device or network)
- Website domain owners
These entities can still monitor and record digital information generated during searches.
Popular Search Engines
- Google: The most popular search engine, with more than 92% of the market share across the world, as per StatCounter. Google’s personalisation algorithms are highly advanced, using machine learning to tailor results based on user data.
- Yahoo: Holds nearly 4% of the market, offering search results with some personalisation features.
- Microsoft Bing: The total share of the market is slightly over 1%; it is used by Windows users to receive personalised search results and is also compatible with Microsoft services.
Personalisation helps search engines deliver a more relevant and efficient search experience, but it also raises privacy concerns. Users can control some personalisation settings, limit data collection, or use privacy-focused engines like DuckDuckGo for less tracking.
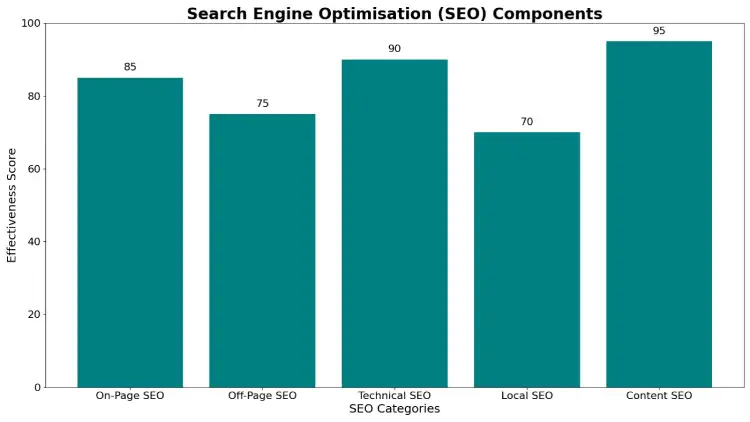
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) is the process of enhancing a website’s visibility and ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs) for specific keywords and search queries. The goal of SEO is to attract more organic (unpaid) traffic by ensuring that a website is relevant, authoritative, and user-friendly.
While SEO is most commonly associated with internet search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo, its principles can also be applied to specialised search engines that focus on images, videos, or other types of content. In these contexts, SEO techniques are adapted to improve the visibility of non-textual content, such as optimising video titles, descriptions, tags, and image alt text. Despite these variations, the core principles of SEO—relevance, authority, and usability—remain consistent.
“Want to boost your website’s ranking and traffic? At TechishWeb, we provide expert SEO services tailored to your business. Get started today!”
Types of SEO
SEO can be divided into several main subtypes, each focusing on different aspects of website optimisation:
1. Technical SEO
Technical SEO focuses on optimising the technical aspects of a website to improve search engine crawling, indexing, and user experience. Key considerations include:
- WebsiteMargins: Quick navigation enhances uuser experienceand also optimisation of search ranking.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Mobile-optimised sites are more preferred on mobile search results.
- Site Architecture: Clear navigation, structured URLs, and internal linking make it easier for search engines to index content.
- HTTPS Security: Secure websites build trust and are ranked higher by search engines.
- XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt: These guide search engines on which pages to crawl and index.
2. On-Page SEO
On-page search engine optimisation is all about optimising a single page of the website to achieve the number one ranking position and receive the targeted traffic. Elements of on-page SEO include:
- Keyword Optimisation: Using relevant keywords naturally in the title, headers, and content.
- Meta Tags: Optimising meta titles and descriptions for clarity and click-through rate.
- Header Tags (H1, H2, H3): Organising the content to make it easy to digest as well as optimise search.
- URL Structure: Development of SEO-friendly URLs which are short, descriptive and rich in keywords.
- Content Quality: Publishing original, informative, and engaging content that satisfies user intent.
3. Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO refers to activities conducted outside the website to enhance its authority and ranking. These include:
- Backlink Building: Acquiring high-quality links from reputable websites.
- Social Media Engagement: Promoting content through social platforms to increase visibility and traffic.
- Influencer Outreach: Cooperation with business influencers to increase the reach and trustworthiness.
- Brand Mentions: Gaining recognition and authority through mentions on authoritative sites.
Importance of SEO
Effective SEO helps websites:
- Increase organic traffic from search engines
- Improve website authority and credibility
- Enhance user experience through technical optimisation
- Achieve long-term visibility without relying solely on paid ads
By combining technical, on-page, and off-page strategies, businesses and content creators can maximise their chances of ranking higher on SERPs, reaching their target audience, and achieving sustainable online growth.
New Trends in Search Engines
The world of search engines is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing user behaviour, and growingprivacy concernsy. Several emerging trends are shaping the future of how search engines operate and how users interact with them. Understanding these trends is essential for businesses, content creators, and developers who want to stay ahead in digital marketing and SEO.
1. Zero-Click Searches
Zero-click searches are becoming increasingly common. In these searches, users get the information they need directly on the search engine results page (SERP) without having to click on any link. Examples include featured snippets, knowledge panels, weather forecasts, or quick calculations.
- Generative AI Integration: Advanced AI systems can gather information from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive answer directly on the SERP. This reduces the need for users to visit external websites and emphasises the importance of appearing in featured snippets for SEO.
2. AI-Powered Personalisation
Search engines are leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to deliver highly personalised results. AI algorithms consider a user’s behaviour, preferences, search history, and contextual factors such as location and device type.
- Improved User Experience: Personalised results increase relevance and engagement. For businesses, this means targeting content and advertisements more effectively.
- Adaptive Learning: AI systems continuously learn from user interactions to refine recommendations and optimise search relevance.
3. Voice Search and Natural Language Processing (NLP)
The rise of voice-activated devices like smart speakers, smartphones, and virtual assistants is transforming search behaviour. Users increasingly perform conversational queries rather than typing short keywords.
- NLP Improvements: Search engines are improving their understanding of natural language, enabling them to interpret complex, conversational questions.
- SEO Implications: Content must be optimised for voice search by including natural, question-based phrases that reflect how people speak.
4. Privacy-Focused Search Engines
Growing awareness of digital privacy is driving interest in search engines that prioritise user data protection.
- Anonymous Search Options: Users are seeking platforms that do not track search history, store personal information, or target ads based on behaviour.
- Examples: DuckDuckGo and other privacy-focused engines are gaining popularity as people become more concerned about data security.
5. Visual and Multimodal Search
Visual search allows users to search using images or videos instead of—or in addition to—text.
- Multimodal Search: Future search engines will increasingly combine text, images, and video inputs to allow more complex and accurate queries.
- Applications: Shoppers can search using a product image to find similar items, while researchers can analyse visual content to locate sources or related material.
6. Question-Answering and Featured Snippets
Search engines are increasingly displaying quick answers at the top of SERPs, often called featured snippets or rich answers.
- SEO Strategies: Optimising content for question-answering is becoming a key SEO tactic. Providing clear, concise answers to common queries can improve visibility in featured snippets.
- User Benefits: Users can get immediate answers to their questions without scrolling through multiple pages, improving overall search efficiency.
7. Future Implications
These trends collectively indicate a shift in how search engines prioritise relevance, speed, and user experience:
- Websites must focus on structured data, concise answers, and visual content.
- Businesses need to adapt SEO strategies for AI-driven personalisation, voice search, and zero-click results.
- Privacy considerations and multimodal search are likely to influence user trust and engagement significantly.
In summary, the future of search engines will be defined by AI, personalisation, voice and visual search, privacy, and immediate access to information. Staying informed about these trends is essential for anyone looking to maximise online visibility and maintain relevance in an increasingly competitive digital landscape.
Search with Elastic
Elastic is a powerful platform for building personalised, scalable, AI-driven search experiences. It supports:
- Textual, Vector, and Hybrid Search: Combines keyword and semantic understanding for accurate results.
- Generative AI Integration: Provides intelligent answers, summaries, and recommendations.
- NLP Transformer Models: Enable language understanding, sentiment analysis, and intent detection.
- Third-Party Model Management: Integrates external AI models for advanced search capabilities.
Elastic is trusted by businesses to create fast, intelligent, and highly relevant search experiences across websites, apps, and enterprise platforms.
Demystifying the Search Algorithm
Search engine algorithms are complex rules that determine which results appear on the search engine results page (SERP) and in what order. Key points include:
- Relevance: Algorithms aanalysehow closely a webpage matches a user’s query using keywords and semantic context.
- Content Quality and Authority: Pages with credible backlinks, expert authors, and high-quality content rank higher.
- User Experience: Factors like page speed, mobile-friendliness, navigation, and HTTPS security impact rankings.
- Indexing: Search engines crawl and index websites to organise content for quick retrieval.
- Personalisation: Results may be tailored based on location, search history, or device type.
- Continuous Updates: Algorithms are regularly updated to improve accuracy, user satisfaction, and fight spam.
- SEO Importance: Understanding algorithms helps optimise websites for higher visibility and organic traffic.
This approach ensures users receive the most relevant, trustworthy, and useful search results.

Final Thought
Search engines have revolutionised how we find information, and staying updated on SEO, AI personalisation, and emerging search trends is key to online success. By optimising for relevance, quality, and user experience, businesses can boost visibility, build trust, and connect effectively with their audience in today’s digital world.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a search engine?
A search engine helps users find information online by matching keywords with its database. It works through crawling, indexing, and ranking relevant pages.
2. How do search engines make money?
They earn through ads (PPC & contextual), user data, affiliate links, and donations for nonprofit engines.
3. What is search personalisation?
Search engines use user data like history, location, and preferences to tailor results, ads, and recommendations. Cookies help track and improve personalisation.
4. What is SEO?
SEO improves a website’s visibility on search engines using technical, on-page, and off-page strategies, boosting traffic, authority, and user experience.